The uterus plays an important role in a women’s reproductive health, responsible for the health of her menstrual cycle, ovulation, pregnancy, and fertility. Uterine health is also one of the most frequently discussed topics in women's health. Focusing on uterine health can prevent uterine-related diseases such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and uterine polyps, as well as early detection of uterine cancers, preventing deterioration of the condition, increasing the success rate of treatment, and providing for a woman's overall well-being.

Uterine fibroids are the most common benign tumors that occur in women and are often referred to as leiomyomas. Fibroids affect the normal functioning of the uterus, leading to abnormal bleeding and associated problems, some require myomectomy. However, not all fibroids carry noticeable symptoms. If your overall health is normal without any uterus-related pain, there may not be a cause for significant concern.
The incidence of uterine fibroids is also related to race, according to the report from PMC, women who underwent hysterectomies for non-cancerous conditions reported that black women with uterine fibroids accounted for 89%, with an average of 37.5 years old, compared to with 41.6 years for white women. Moreover, the frequency of fibroids increases with age throughout the reproductive years.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids?
The factors that cause uterine fibroids are not known with certainty but are medically linked to changes in the hormone levels such as estrogen and progesterone, and the muscular structure inside the uterus.
Based on the statistics of cases of fibroids, uterine fibroids can occur mainly in the following groups:
People with high BMI
Hereditary fibroids
People with early first menstruation
Late menopause
People who have never had children
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids can be divided into 4 types based on where they primarily grow, but not exhaustive; categories need to be further divided based on their size as a way of determining the subsequent treatment of it.
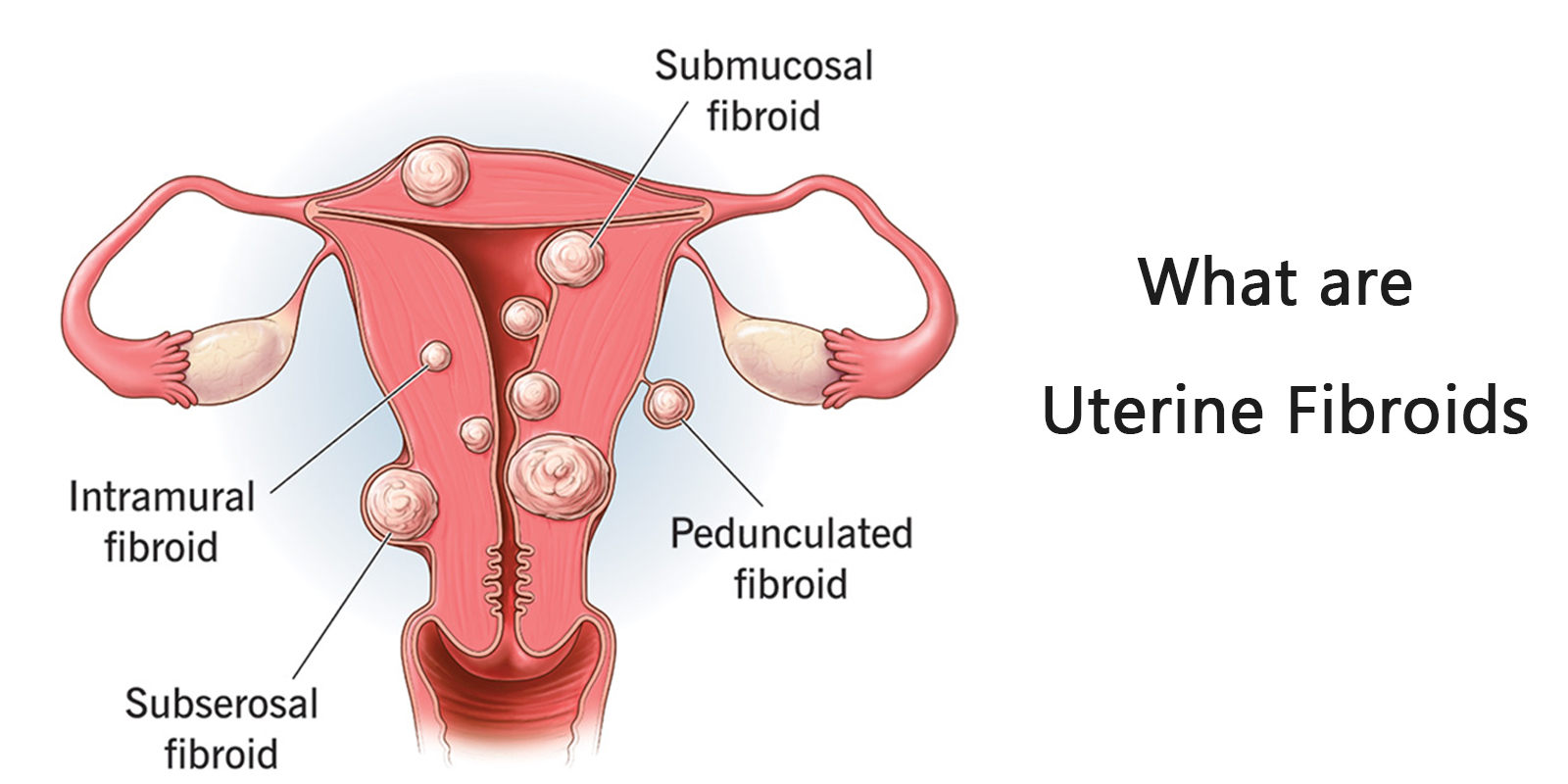 image source: clevelandclinic
image source: clevelandclinic
- SUBSEROSAL FIBROIDS
Subserosal fibroids grow towards the plasma of the uterus, protrude from the outer surface of the uterus, and are surrounded by a muscular layer on their surface, with a prevalence of around 20%. They grow on the outer surface of the uterus and mostly continue to grow outwardly, so there are rarely any obvious uterine-related symptoms in response to them.
However, large subplasma fibroids may compress nearby organs, such as the bladder and rectum, resulting in high-frequency urination and constipation.
- SUBMUCOSAL FIBROIDS
Submucosal fibroids grow towards the uterus, protrude from the surface of the uterine cavity, and are covered by the mucous membrane. The incidence of these fibroids ranges from 10% to 15%, and they can cause uterine contractions, with heavy and irregular bleeding, which can lead to infertility, difficulty in conceiving, and miscarriage.
- INTRAMURAL FIBROIDS
Intermural fibroids are fibroids that grow inside of the uterus, posited at the muscle surface, and are surrounded by muscle tissue, with an incidence of 60% to 70%. Improper location and excessive size may cause heavy bleeding from the uterus, low chances of pregnancy, and greater chances of miscarriage.
- PEDUNCULATED FIBROIDS
A pedunculated leiomyoma is a variant of a subglacial or submucosal leiomyoma. Some of the subglacial fibroids form stems as they grow, creating a pedunculated fibroid, which usually leads to infertility.
Regular uterine ultrasounds can prevent fibroids from growing too large and reduce their impact on reproductive health.
Symptoms of Fibromas in Uterus?
- Irregular periods.
- Abnormal bleeding.
- Bloating and feeling like your abdomen is protruding.
- Frequent urination or constipation: this may happen when the fibroid presses on the bladder.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Low chance of conception.

If you’re pregnant, fibroids in large size can increase the risk of miscarriage.
Other Conditions of Uterus
Besides fibroids, what are some common diseases of the uterus?
Uterine polyps: growths within the lining of the uterus.
Uterine cancer: Cancer of the uterus, such as endometrial cancer or uterine sarcoma.
Endometriosis: a condition in which the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus.
Pelvic inflammatory disease: an infection of the reproductive organs
Uterine prolapse: a condition in which the uterus slips out of position.
How Can Fibroids Affect Pregnancy?
The size and position of uterine fibroids can affect the pregnancy and labor process in various aspects. For TTC women and moms-to-be with fibroids, prenatal physical exams, and proper pregnancy management are critical. Conditions may arise during pregnancy that require treatment of fibroids for getting a smooth labor and preventing complications. If you have large or multiple fibroids, please focus on the following issues when you are pregnant:

Problems with placental abnormalities
Placental abruption: fibroids may disrupt the normal attachment of the placenta to the wall of the uterus, leading to placental abruption, which can be dangerous for both mother and baby.
Abnormal prenatal presentation: Large fibroids can sometimes prevent the baby from positioning itself properly in the uterus, resulting in a breech or transverse position, which may require a cesarean section.
Problems with Fibroids Getting Bigger:
Studies have shown that about two-thirds of fibroids will grow or shrink during pregnancy. If growth occurs, it usually happens during the first trimester of pregnancy. Your OB/GYN may check the size of the leiomyosarcoma with an ultrasound to monitor changes and assess the baby's growth. To date, studies have not shown an absolute correlation between leiomyomas and fetal growth restriction.
Labor Problems
Preterm labor: A severe burden of fibroids may put pressure on the uterus, leading to preterm contractions or premature rupture of membranes (when your water breaks before 37 weeks) and subsequent labor. It is important to contact your OB/GYN if you think you may be in labor or leaking fluid.
Preterm labor: Fibroids may trigger contractions and lead to preterm labor, increasing the risk of preterm delivery.
Difficult labor: In some cases, fibroids may block the birth canal, making vaginal delivery difficult or impossible and requiring a cesarean section.
How to Treat Uterine Leiomyomata?
Maintaining the habit of medical checkups can prevent uterine fibroids from reaching a large size, but the enlargement of them does not mean a necessary removal, To decide whether or not surgical removal is necessary should according to the doctor's advice, and mainly depends on the location of the fibroids. For most fibroids that are small and do not cause harm to the body, medication and dietary regimens are sufficient.
Medication:
Pain Medications? Pain medications such as ibuprofen can temporarily relieve your pain and abdominal soreness from fibroids.
Supplements? Excessive bleeding may cause iron insufficient in your body, so proper iron supplements can be helpful in these situations.
Birth control pills: Birth control pills are one of the mainstay means of birth control, and are beneficial in relieving the symptoms of heavy menstrual bleeding, and menstrual cramps that can be associated with uterine fibroids.
Fibroid removal surgery?
Different sizes and locations of fibroids will determine the type of removal surgery. The choice of whether or not to undergo a hysterectomy during a fibroid removal surgery is usually based on your wishes, and by removing the uterus, you give up the possibility of future pregnancies.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a safe and effective treatment that uses microwave (RF) energy to treat fibroids and is suitable for removing and treating smaller fibroids.
Track Women’s Health
Uterus-related diseases remind women of the importance of regular medical checkups, but in recent years, women have become increasingly interested in data-driven health monitoring to keep track of their health and make timely adjustments to their lives and work. The devices used to track women's health have changed from watches and wristbands to more wearable everyday wear such as smart ring. These ovulation trackers provide reproductive health indicators such as menstrual cycle, ovulation prediction, pregnancy monitoring, and sleep health, enabling women to detect potential problems early and prevent various diseases. These wearable fertility trackers also provide specialized scientific articles about women's health to raise women’s health awareness, and better protect themselves.

In addition to women themselves, the resources allocated by society for women's health also need to be increased. Sharing sessions on women's health are held in the community to supplement and improve the existing healthcare policies regarding the differences and deficiencies in women's health. Through the popularity of public health care policies to raise awareness of women's health, resources will reach out to different groups of women to improve women's health as a whole.
Femometer, as a women's health brand, is dedicated to providing women with the most accurate health data, the most comfortable ovulation tracker, and the most comprehensive women's health knowledge. To make women free themselves from the discomfort of wearing a wristwatch, Femometer offers a smart ring that can be worn at night to monitor your basal body temperature and sleep conditions, and the data is synchronized to the Femometer App to give you the most accurate ovulation prediction and sleep analysis. Its long battery life also guarantees you at least 10 days of burden-free use, and the convenient and fast charging settings won't interfere with your plans to monitor your health in the long run.
This article is the original creation of Femometer. All rights reserved by Femometer Inc. To reproduce, distribute, or reference the content, please reach out to us in advance to prevent any potential legal issues. Copyright © Femometer Inc.