As summer arrives, the temperature rises, and people who love sports are increasingly beginning outdoor activities. However, women who are fitness enthusiasts or trying to lose weight these times may have problems with late periods, with less frequent bleeding, because the sudden change to high-frequency sports and weight loss will have an impact on the women’s ovarian function, which will lead to irregular periods.
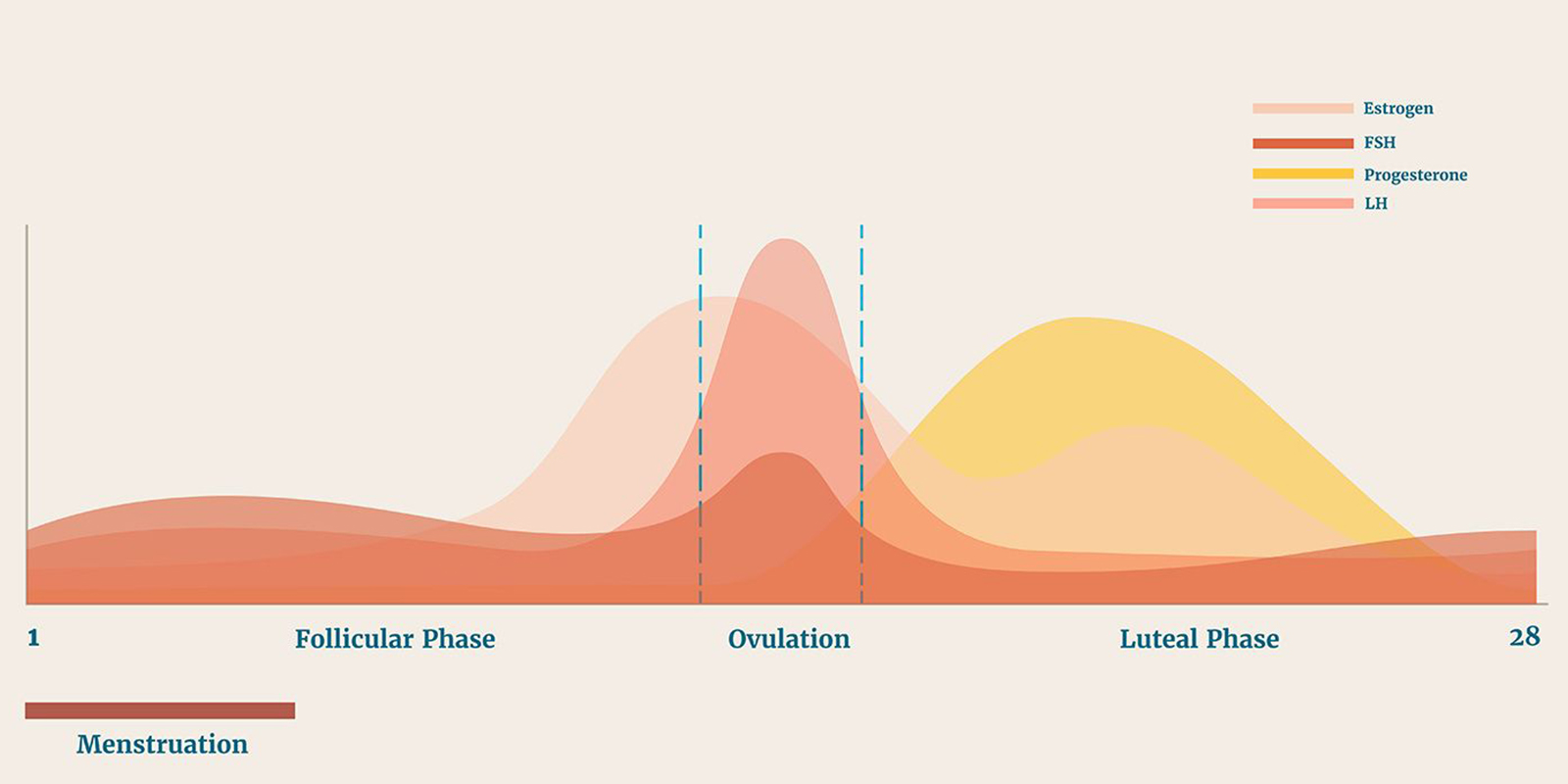 Image source : everydayhealth
Image source : everydayhealth
Normal Menstrual Cycle
What is a late period and how long is considered a delayed period? How much bleeding is considered normal? Research from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) shows that a normal menstrual cycle lasts 21-37 days, with an average blood loss of about 30-40ml. The average menstrual cycle usually lasts 28 days, 24-28 days are considered normal. However, if the length of your menstrual cycle is less than 21 days or longer than 37 days, it may mean that you have an underlying health problem and it is recommended that you seek medical help to ensure your health.
Factors Associated with Menstrual Cycle Irregularity
1. Obesity
A study from PMC analyzed the effects of smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and stress levels on menstrual cycle and menopause by selecting data from adult women aged 19 years and older who were selected to participate in the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007-2014. The results indicated that women with a BMI of 25-30 or exceeding 30 had a higher likelihood of menstrual irregularities, which is consistent with the results of previous studies on the relationship between menstrual irregularities and obesity. For example, a study involving 14,779 women aged 19-23 years showed that those with BMI < 17, 17-18.5, 18.5-20, and 25-30 have 1.4 times more probability of having irregular menstrual cycles compared to those with BMI 20-25, respectively.

The mechanism for the association between BMI and irregular menstruation may be attributed to lower levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and higher levels of testosterone and FAI. Current research suggests that women with higher BMI experience irregular menstruation due to lower levels of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and higher levels of testosterone, FAI, and insulin. An increase in BMI results in a decrease or increase in SHBG, testosterone, FAI, and insulin.
2. Excessive stress
High levels of perceived stress have also been shown in studies to be associated with a high probability of irregular menstrual cycles. According to a study that utilized a special tool to examine stress levels in college students also indicated that stress is associated with irregular menstruation. One theory that explains the mechanism by which stress affects the menstrual cycle proposes the HPA axis. The theory suggests that a decrease in the activity of the HPA axis leads to the onset of menopause. When stress levels are high, HPA axis activity is interrupted. As a result, women with higher levels of stress are more likely to experience irregular periods than women without stress.

3. Smoking
No studies have shown the specific effects of smoking on menstrual irregularities yet. However, in terms of statistical analysis, smokers were 1.4 times more likely to have menstrual irregularities than non-smokers when controlling for univariate variables.
Smoking involves variant factors such as lifetime smoking status, secondhand smoke, daily cigarette consumption, age of smoking initiation, and number of packs smoked per year. Every situation has different influences on menstrual irregularities.
4. PCOS
Menstruation is related to the uterus's health, uterine-related disorders may also cause irregular menstruation.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries are unable to produce enough hormones for ovulation, resulting in an absence of ovulation, in which many small cysts form in the ovaries and these cysts secrete androgens, which leave the woman's body with an overabundance of androgens. PCOS can cause problems with a woman's menstrual cycle with many symptoms, including hair loss, chronic fatigue, and irregular or even no periods at all.
Menstruation is influenced by the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, which causes the endometrium to respond cyclically, leading to period bleeding. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine metabolic disease in which the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis is dysfunctional, the patient may have scanty or persistent ovulation, and the body is unable to produce progesterone, and the endometrium is only affected by a single estrogen, not progesterone, resulting in reduced or no shedding of the endometrium, and irregular menstruation, some scanty or infrequent menstrual cycles in less severe cases and amenorrhea in severe cases. In severe cases, amenorrhea may occur.
Patients may also notice an abnormal level of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, the marked increase in androgen production mainly causes amenorrhea.
Patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased secretion of androgens, and often have external manifestations such as acne, obesity, hairiness, and rough skin. The psychological stress of some of the patients may also affect the endocrine system, which may lead to a lack of menstruation.
PCOS can also lead to heavy bleeding during menstruation. Bleeding exceeds 80ml and clotting occurs.
5. Medicine Intake
Progesterone medications: such as dydrogesterone tablets and medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets can be used mainly for conditions of dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, and irregular menstrual cycles. They can raise the hormone level in the body so that the endometrium does not shed as well as bleed, resulting in a late period, while regulating the value of progesterone in women's bodies, changing the physiological environment of the endometrium, making it transform from preproduction to secretion, inhibit ovarian ovulation, prolong the time of ovulation and delay menstruation, to make menstruation delayed, and cause menstrual disorders if long-term use;
Short-acting contraceptives: such as medroxyprogesterone ethinyl estradiol tablets, menstruation is a significant symbol of reproductive function maturity, usually the endometrium cycle of shedding and bleeding, and short-acting contraceptives can inhibit ovulation, and change the uterine lining, to play a contraceptive role, but also to make menstruation prolonged and delayed. Please take medicine under the guidance of your doctor.
Foods that Cause Your Late Period
- Spicy food;
- Lemon or lime Juice;
- Veggies, legumes, and some grains that rich in phytoestrogens;
- Gelatin, it is said that dissolving gelatin in warm water and drinking it can delay menstruation for up to 4 hours, but no specific studies are showing the effectiveness of gelatin in delaying the principle of menstruation, and over-consumption of gelatin can have side effects.

How to Get Pregnant with Irregular Periods?
Ovulation is not equal to menstrual bleeding, the scars on your uterus(if you have one) or some hormonal medications may cause a situation like ovulation to be normal but not produce bleeding. Similarly, bleeding similar to a period that occurs in a time does not exactly mean ovulation because the overly thick uterine lining and unstable hormone levels can also cause bleeding in the uterus. Irregular periods are also not a sign that the ovaries are not functioning to ovulate, and correctly predicting the precise time of ovulation can raise your pregnancy possibility to 90%.
How to Track Ovulation With Irregular Periods?
- Monitoring specific hormones (LH Hormone Level)
Luteinizing hormone levels will rise sharply just before ovulation, making monitoring luteinizing hormone levels a significant method for those who need to prepare for pregnancy but have irregular periods. Traditional LH hormone tests require a good understanding of test line intensity, although they are widely used, the results may influenced by subjective factors. Femometer IVY103 provides a clear digital display, solving these problems and providing women with a clear luteinizing hormone monitoring kit.
- Tracking Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
The Basal Body Temperature (BBT) method is used by 90% of TTC users in tracking ovulation, and or for contraception. BBT tracking has gradually evolved from the old method of oral temperature measurement before getting up, to nighttime continuous tracking with smart wearables such as smart rings. These smart rings can be connected to an ovulation tracking app that predicts the ovulation time by accurately measuring the finger temperature with over 99% accuracy, with valuable insights about women's health provided in the app, helping women keep an eye on their reproductive health status. All you need to do is wear the smart ring before bed.
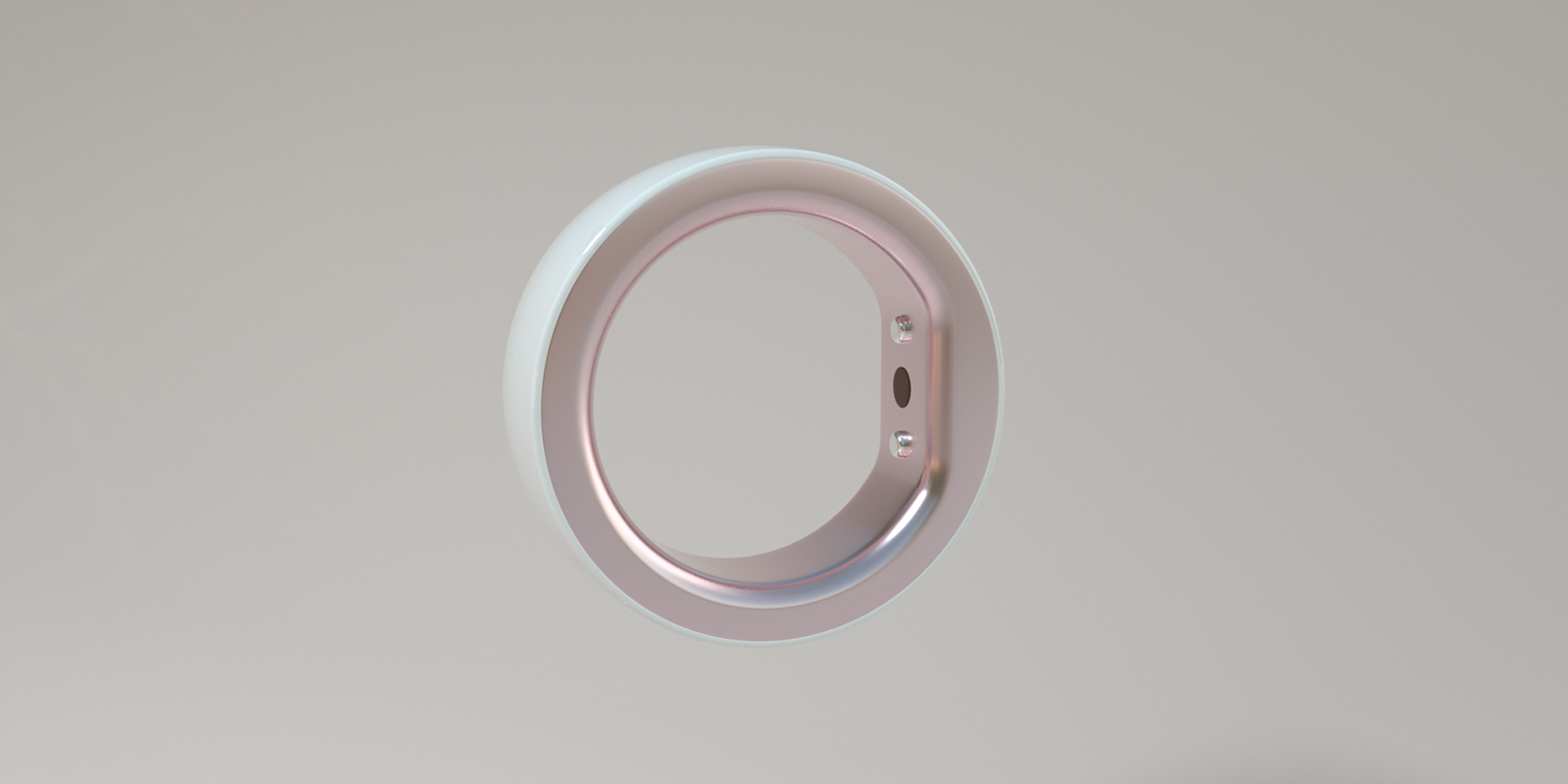

Irregular menstrual cycles do not equal infertility. Digital wearable technology can provide you with the most accurate fertility window.
How to Regulate Your Periods?
- Practice Yoga
Yoga provides you, not just relaxation, but also effective results in regulating menstruation. A 2017 study stated that consistent practice of yoga for 12 weeks improved bloating and breast pain that occurs during menstruation and was also effective in regulating the menstrual cycle.
Yoga has also been shown to reduce pain and emotional symptoms associated with menstruation, such as depression and anxiety, and improve the quality of life for women with primary dysmenorrhea.
- Maintain a healthy weight
As mentioned above, sudden weight loss or gain can lead to irregular periods. That's why it's important to maintain a moderate weight.
If you want to lose weight, keep it slow and healthy, or consult your doctor or dietitian to help you set a target weight and develop strategies to achieve it.
- Diet and Supplements
A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle can regulate your body's hormone levels and strengthen your resistance to menstruation irregularity. Likewise, taking the right amount of supplements will help you to strengthen your health.
- Iron-rich foods: Iron-rich foods such as meats, vegetables, and soybeans can replenish your body's iron levels to counteract the loss of iron caused by menstrual bleeding.
- Squid Extract: Rich in B vitamins and minerals, it helps to relieve symptoms caused by menstrual irregularities such as menstrual pain and mood swings.
- Fish Oil: rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, helps reduce inflammation, regulates the endocrine system, and promotes normal menstrual bleeding.
- Vitamin B: Vitamin B, including vitamin B6 and vitamin B12, helps regulate endocrine balance and relieve anxiety and mood swings. Foods such as whole wheat bread are also rich in vitamin B.
Takeaway
Tracking menstruation and ovulation is not only a need for TTC users but also for women who have late periods to focus on their reproductive health. Continuously recording your menstrual cycle through products such as the menstrual cycle monitoring app and the Smart Ring enables you to take control of your uterine health and menstrual cycle problems. Thus, if you experience a prolonged late period without getting pregnant, please seek medical attention; if you’re preparing for pregnancy with irregular menstruation, try Femometer ovulation tracker to improve your pregnancy preparation success rate to 99%!
This article is the original creation of Femometer. All rights reserved by Femometer Inc. To reproduce, distribute, or reference the content, please reach out to us in advance to prevent any potential legal issues. Copyright © Femometer Inc.