Progesterone is a crucial hormone in a woman's body, playing a pivotal role in regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting pregnancy. Produced primarily by the ovaries following ovulation, progesterone helps prepare the uterus for implantation and supports the early stages of pregnancy by maintaining the uterine lining. This hormone also plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy by preventing contractions of the uterine muscles that could lead to miscarriage.
When progesterone levels are low, it can significantly impact a woman's fertility and reproductive health.
Symptoms of Low Progesterone
Here are some common symptoms of low progesterone:
Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Changes in menstrual patterns, including irregular periods, shorter menstrual cycles, or spotting between periods, may indicate low progesterone levels.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding:

Low progesterone can lead to heavier or prolonged menstrual bleeding during periods.
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) Symptoms:
Increased severity of premenstrual symptoms such as mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression, breast tenderness, bloating, and headaches may occur with low progesterone levels.
Low Libido:
Hormonal imbalances, including low progesterone levels, can affect libido or sexual desire in some individuals.
Fatigue:
Feeling excessively tired or fatigued, especially during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, may be associated with low progesterone levels.
Insomnia or Sleep Disturbances:
Changes in sleep patterns, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, may occur with hormonal imbalances such as low progesterone.
Mood Swings and Anxiety:
Fluctuations in progesterone levels can impact neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to mood swings, anxiety, or feelings of depression.
Headaches or Migraines:
Some individuals may experience an increase in headaches or migraines associated with hormonal fluctuations, including low progesterone levels.
Diagnosis of Low Progesterone Symptoms
It's important to note that these symptoms may vary from person to person, and other factors or underlying health conditions may contribute to similar symptoms.
Medical History Assessment:
Your healthcare provider will ask about your menstrual history, including the length and regularity of your menstrual cycles, as well as any symptoms you may be experiencing that could indicate hormonal imbalances.
Physical Examination:
A physical examination may be performed to assess any physical signs or symptoms associated with low progesterone levels, such as breast tenderness, acne, or abnormal hair growth.
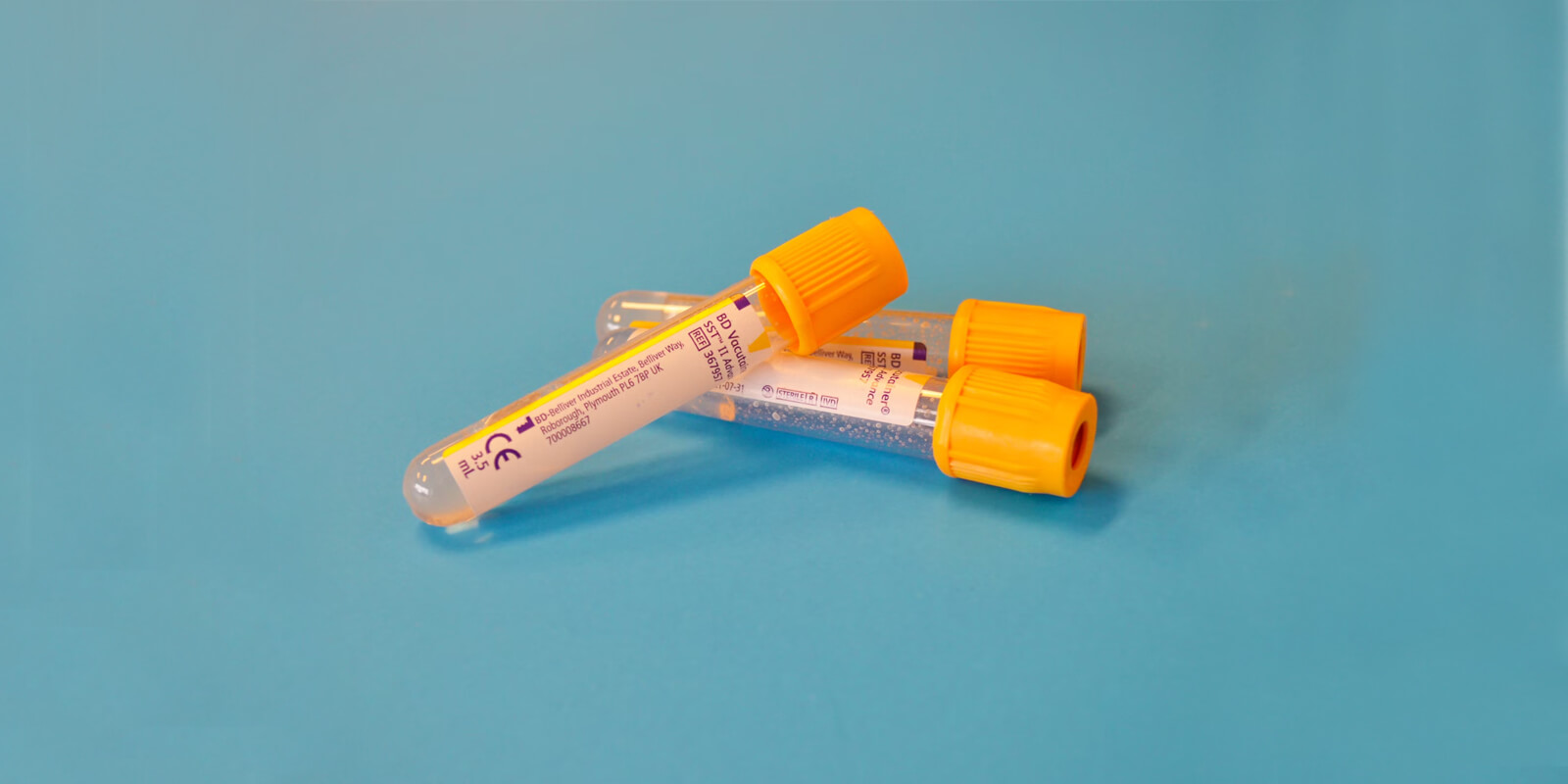
Blood Tests:
Blood tests are the most common method used to measure progesterone levels. A sample of blood is drawn and analyzed to determine the concentration of progesterone in your bloodstream. This test is usually performed during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, typically 7 days before the expected start of your next period.
Saliva Tests:
Some healthcare providers may recommend saliva tests to measure progesterone levels. Saliva tests are non-invasive and can be done at home using a saliva collection kit. However, the accuracy of saliva tests for progesterone measurement is still debated within the medical community.
Ultrasound:
In some cases, an ultrasound may be used to assess the thickness of the uterine lining, which can indirectly indicate progesterone levels. A thin uterine lining may suggest inadequate progesterone production.
Endometrial Biopsy:
In certain situations, an endometrial biopsy may be performed to assess the uterine lining for signs of inadequate progesterone support. This procedure involves taking a small tissue sample from the lining of the uterus and examining it under a microscope.
Effect of Low Progesterone Symptoms on Women's Fertility

Low progesterone levels can significantly impact women's reproductive health and fertility, leading to various symptoms and complications that can affect conception and pregnancy outcomes:
Missed or Late Periods:
Progesterone plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle. Insufficient progesterone levels can result in irregularities in the menstrual cycle, such as missed or late periods.
Uterine Bleeding or Spotting:
Inadequate progesterone support can cause abnormal uterine bleeding or spotting between periods. This irregular bleeding may occur due to the instability of the uterine lining, which is essential for embryo implantation and pregnancy maintenance.
Late Ovulation:
Progesterone is essential for triggering ovulation and preparing the uterine lining for implantation. Low progesterone levels may delay ovulation, leading to irregular or late ovulation cycles, which can reduce the chances of conception.
Infertility:
Progesterone plays a vital role in supporting early pregnancy by maintaining the uterine lining and preventing its shedding. Insufficient progesterone levels can impair embryo implantation and increase the risk of infertility, making it challenging to achieve pregnancy.
Miscarriage:
Inadequate progesterone support during early pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage. Progesterone helps maintain the uterine environment necessary for embryo implantation and fetal development. Low progesterone levels may result in a weakened uterine lining, making it difficult for the embryo to implant properly and sustain a pregnancy.
How to Increase Progesterone Levels Naturally?
Here are some ways to naturally increase progesterone levels.
Natural Progesterone Cream:
Natural progesterone cream, derived from plant sources, is applied topically to the skin. It can help supplement progesterone levels in the body and support hormonal balance. However, it's essential to use these creams under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure proper dosage and application.
Hormone Balancing Supplements:
Supplements like inositol, a type of B vitamin, can help promote hormonal balance and support progesterone production. Femometer's Inositol supplement is specifically formulated to support women's reproductive health and hormonal balance, providing a convenient and effective way to increase progesterone levels naturally.
Foods High in Progesterone:
Certain foods contain nutrients that support progesterone production and hormonal balance. Examples include beans, broccoli, whole grains, and foods rich in vitamin B6, zinc, and magnesium. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help naturally increase progesterone levels over time.
Healthy Lifestyle Practices:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for supporting hormonal balance and overall well-being. Practices such as getting an adequate amount of sleep, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise can help regulate hormone levels, including progesterone. Femometer's Smart Ring can track your sleep patterns, providing valuable insights into your sleep quality and helping you make adjustments to improve overall health and hormonal balance.
Stress Management:
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels, including progesterone. Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and spending time in nature can help lower stress levels and support progesterone production naturally.
Incorporating these natural methods into your daily routine can help support progesterone production and hormonal balance. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements or making significant lifestyle changes, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are pregnant. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs and monitor your progress to ensure optimal results.
This article is the original creation of Femometer. All rights reserved by Femometer Inc. To reproduce, distribute, or reference the content, please reach out to us in advance to prevent any potential legal issues. Copyright © Femometer Inc.